Adults aren’t the only ones who need vitamin D supplementation. If your kids aren’t supplementing, they are likely to be deficient, which can have serious health consequences, especially related to immunity.
- When D levels fall below 20, the immune system response is impaired. This has been proven in children through repeated studies:
- In the US, 50% of children aged 1-5 and 70% of those aged 6-11 are vitamin D deficient (level <20) or insufficient (<30) while optimal levels are between 40-70.
- Infants with vitamin D levels <20 were 5x more likely to develop RSV in the first year of life, compared to those with D levels >30.
- Children given 1200 IU vitamin D from December through March were 58% less likely to contract influenza A. Even those with asthma were less likely to become sick.
- Children who took vitamin D daily had a relative risk reduction of 93% for having an asthma attack compared to kids who didn’t supplement.
- For kids with asthma taking budesonide, adding vitamin D resulted in fewer asthma exacerbations since vitamin D reduced the incidence of upper respiratory infections.
- Low vitamin D correlated with allergen sensitivity in children with eczema. Kids whose D level was < 15 were more likely to have peanut, ragweed and oak allergy.
- Vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency occurs in 27-91% of all pregnant women in the US. Optimal levels for pregnancy are 2000-4000IU/day. Breast milk contains very little vitamin D so moms need to continue to supplement and optimal levels in the literature point to closer to 4000 IU/day. Newborns with low vitamin D were more likely to develop upper respiratory and ear infections by 3 months of age and wheezing at 15 months, compared to those with higher levels.
- Moms who took sufficient vitamin D during pregnancy reduced their offspring’s risk for Type 1 diabetes.
- Having adequate D in utero and early stages of life supports normal brain development and mental functioning. Low vitamin D levels are frequently found in adolescents with severe mental illness. Vitamin D deficiency is even linked to an increase risk for schizophrenia. Many psychiatric patients have shown clinical improvement with vitamin D supplementation. In human studies, resolution of depression occurred when depressed adolescents were adequately supplemented.
- Low vitamin D leads to reduced absorption of calcium which can adversely impact bone development.
- Theories point to a role for vitamin D in autism since it can impact serotonin levels, inflammation, glutathione, and seizures. This does not diminish the genetic or other environmental contributions, but vitamin D deficiency may allow the expression of unfavorable genetic consequences.
- Since body fat can sequester vitamin D, it is now recognized that obese children and adults often require 2-5x more D to treat and prevent deficiency.
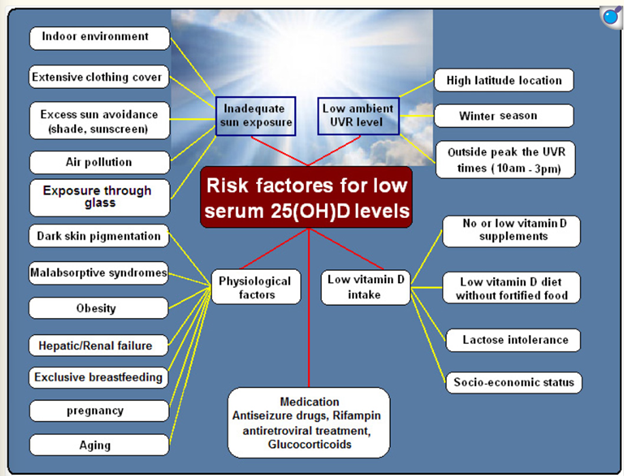
- Vitamin D: Virtually no vitamin D is obtained from the sun in the winter months in the northeast. Even during the summer months, sunscreens reduce vitamin D absorption by 95-99%. Obesity hinders the activation of vitamin D in the body. The ideal range in blood is 40-70 ng/mL.

Comments are closed.